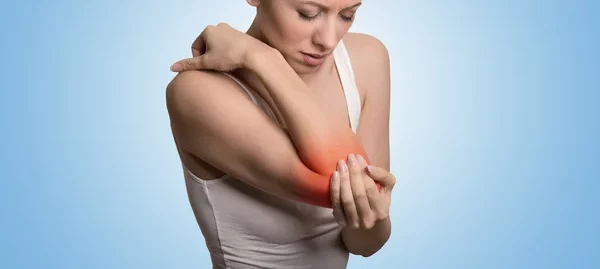
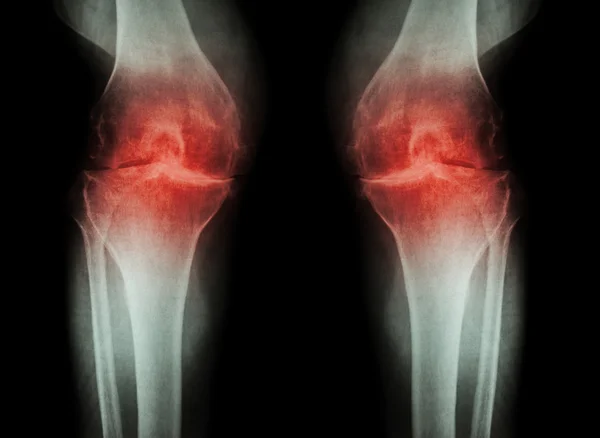
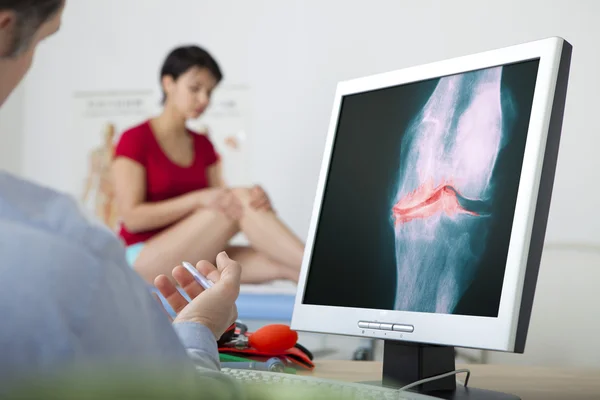
Arthritis is a disorder that causes pain and stiffness in the joints of the body. Living with arthritis can be difficult due to the physical and emotional toll associated with the condition. After all, the pain and stiffness associated with arthritis can significantly limit your movement, quality of life, and overall well-being. There are over 100 kinds of arthritis, but the most common is osteoarthritis. It is estimated that over 32.5 million adults in the U.S. alone suffer from this condition.
Unfortunately, like all forms of arthritis, osteoarthritis has no cure. However, that doesn’t mean you can’t do anything about the symptoms. With proper pain management, you can limit pain and inflammation as well as preserve joint function.
What Is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease. It occurs when the protective cartilage between the bones in the joints wears away, leading to bone-on-bone contact and pain. Osteoarthritis can affect any of the body’s joints, but most commonly affects hands, hips, knees, and spine. As a result, the diagnosis of osteoarthritis can be complex and requires a thorough medical history and physical examination to identify the affected joints.
Anatomy And Pathophysiology Of Osteoarthritis
The following joints are most commonly affected by osteoarthritis, especially as people age:
- Hands: The joints connecting the fingers, thumbs, and wrists are the most frequently affected because of their frequent use. Unfortunately, pain and stiffness in the hands can significantly limit your daily activities.
- Knees: Osteoarthritis in the knee is usually caused by an injury or repetitive use. This can cause pain, swelling, and instability in the affected joint. As a result, walking, climbing stairs, or standing up after sitting for a long time can be challenging if you have knee osteoarthritis.
- Hips: The hip is a major weight-bearing joint prone to osteoarthritis due to age, repetitive use, or injury. As a result, hip pain can be debilitating and make it difficult to do daily activities such as walking and standing.
- Spine: Osteoarthritis in the spine can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. It generally affects the lower back and neck but may also affect the mid-back. When the spine is affected, performing regular activities such as bending over or lifting things without pain can be difficult.
Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis
Symptoms vary based on the location of the affected joints as well as how far the condition has progressed. As such, symptoms can range from mild to severe. With that in mind, the following are the primary symptoms associated with osteoarthritis:
Pain and Swelling
Osteoarthritis typically causes mild to severe pain and swelling in the affected joint that may increase with activity. It occurs due to the inflammation of the joint as well as the destruction of cartilage. When the cartilage is destroyed, the bones can rub against one another, resulting in pain. Swelling typically occurs due to inflammation and fluid buildup in the joint, which is caused by the body’s attempts to repair the joint.
Stiffness and Reduced Range of Motion
Osteoarthritis can cause stiffness and reduced range of motion in the affected joint. Stiffness is caused by inflammation, which makes it difficult to move the joint. This can cause the muscles around the joint to weaken, resulting in further stiffness and reduced range of motion. As a result, moving the joint becomes more difficult. Not to mention, cartilage destruction can limit your range of motion by narrowing the space between your bones, which means your joint will not be able to move as far.
Grating Sensation
A grating sensation may occur when the bones of an affected joint rub against each other. This is due to the destruction of the cartilage, which normally protects and cushions the bones from rubbing against each other. This sensation can be mild to severe and may occur when the joint is moved or touched.
Crepitus
Crepitus, which is the term used for the grating sensation that affects your joints, often indicates a more significant underlying problem. It is the crunching, cracking, or popping sound and sensation felt when your joints move. It can be caused by...
Hot Or Warm Joint
A warm joint occurs when the temperature of your joint is warmer than usual. This can feel like a heat sensation coming from the joint itself, which is often accompanied by swelling, redness, and pain. It could be a sign of an underlying infection if you’re...
Stiffness and Limited Range of Motion
Although it’s normal for people to experience some level of stiffness or reduced range of motion as they age, it may be a sign of an underlying health condition if the issue persists or is causing significant discomfort. When the range of motion of a joint...
Reduced Knee Mobility
In our everyday life, we perform movements such as walking, jogging, climbing stairs, or bending down to tie our shoes almost automatically. And, if we are able to perform these movements, it is thanks to the knee’s complex structure of bones, ligaments,...
Joint Pain And Swelling
Joint pain is arguably one of the most common musculoskeletal complaints among adults of all ages. But the fact that this condition is so widespread does not mean that it isn't life-limiting, or that it should be overlooked. Joint pain and swelling can cause...
Pain In The Lower Back And Legs
Lower back pain can extend beyond the back itself and affect both the gluteal muscles and the many muscles of the legs. This typically occurs as a result of nerve irritation or compression in the lumbar region. When the nerves of the lower back become...
Loss Of Movement In Lower Body
Conditions that cause chronic pain can cause severe damage to important components of the joints, thus limiting your ability to move freely. For example, in patients with arthritis, the sustained high levels of inflammation degrade the joint’s cartilage,...
Back Pain
Back pain is an awful problem that many individuals have encountered. It has the potential to restrict normal mobility and functionality, significantly impacting a person’s quality of...
Pain In Hand And Wrist
Hand and wrist pain can impact day-to-day activities and make it hard to complete necessary tasks. It may be challenging to grip or lift objects, write, type on a computer, or even perform simple everyday tasks like brushing your teeth. Even the most mundane...
Causes And Risk Factors Of Osteoarthritis
The cause of osteoarthritis is still largely unknown. However, several risk factors can increase your chances of developing the condition. These include the following:
Aging
When it comes to osteoarthritis, aging is one of the most common risk factors. As you age, your joints naturally break down, which puts you at greater risk of developing the condition.
Being Overweight Or Obese
Carrying excess weight places extra strain on our joints, increasing the risk of developing osteoarthritis. Excess weight can also increase the pain associated with the condition since the extra weight adds even more pressure to already inflamed joints.
Family History Of Osteoarthritis
Your risk of developing the condition is greater if you have a family history of osteoarthritis. The following is the estimated heritability of osteoarthritis in various parts of the body:
- Osteoarthritis of the knee is 40 percent
- Osteoarthritis of the hip is up to 60 percent
- Osteoarthritis of the hand is 65 percent
- Osteoarthritis of the spine is 70 percent
Repetitive Stress On A Joint
Repetitive stress on a joint can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis, as it can cause wear and tear to the cartilage. Examples of activities that can cause repetitive stress on a joint include running, weightlifting, and playing a sport such as tennis or basketball.
History Of Injury Or Joint Surgery
Injury to a joint, especially one that has not healed correctly, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis. Additionally, joint surgery can increase the risk of developing the condition, as it can disrupt the normal function of the joint.
How Is The Condition Diagnosed?
Osteoarthritis is usually diagnosed by a physical examination and imaging tests. During the physical exam, your doctor will look for signs of swelling, tenderness, warmth, and decreased range of motion in the affected joint. X-rays and/or MRI scans may also help diagnose the condition. X-rays can show bone loss, narrowing between joints, or bone spurs, which can indicate the presence of osteoarthritis. MRI scans can be used to assess the condition of the cartilage and soft tissue around the affected joint.
Getting an accurate diagnosis of osteoarthritis is crucial to determine the best course of treatment. Osteoarthritis is a chronic condition; therefore, proper management is necessary to reduce pain and improve joint function.
Treatment Options For Osteoarthritis
Even though there is no cure, there are various ways you can treat osteoarthritis to improve the condition, whether by reducing inflammation, reducing pain, or improving your range of motion. The following are some of the different ways in which traditional doctors will typically treat osteoarthritis:
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Doctors often prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to treat osteoarthritis. These medications, which include ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin, help reduce inflammation and pain in the affected joint. Additionally, corticosteroid injections may also be used to reduce inflammation and pain.
But, of course, the problem with NSAIDs and corticosteroid injections is that they can have serious side effects. These include allergic reactions, headaches, stomach ulcers, dizziness, and, in rare cases, more severe issues, such as problems with your kidneys, liver, or heart.
Physical, Occupational, And Exercise Therapy
Physical and occupational therapy can help improve joint function, reduce pain, and increase strength. Therapists can teach patients how to perform exercises to increase their range of motion and strengthen the muscles around the affected joint. Additionally, occupational therapists can help adjust daily activities to reduce stress on the joint, and provide adaptive equipment to help make tasks easier.
Surgical Procedures
Surgery may be recommended if the osteoarthritis has progressed to a point where the joint is significantly damaged, and other treatments are not providing relief. That being said, surgery should be a last resort due to its inherently risky nature. Like any form of surgery, there are several drawbacks. Surgery can be expensive, take a long time to recover from, result in various complications (such as infection or nerve damage), and may not even be successful in alleviating pain.
Keeping this in mind, the following are some of the surgical procedures that may be used to treat osteoarthritis:
- Arthrodesis: Arthrodesis is a surgical procedure in which two bones are fused together using metal plates and screws. The goal is to reduce pain and improve joint stability. However, the procedure can limit the range of motion and may result in stiffness.
- Osteotomy: Osteotomy is a type of surgery in which the bone around the knee joint is cut and shifted to take pressure off the affected area. The goal of this procedure is to reduce pain and improve joint function.
- Arthroplasty: This is a procedure in which the affected joint is removed and replaced with an artificial joint. This procedure aims to improve the range of motion and reduce pain. The risk with this procedure is that it can be complicated and may require a lengthy recovery period.
How Neurofunctional Pain Management Approaches Osteoarthritis
We avoid the potential risks and side effects of pain medication and surgery by focusing on a Neurofunctional Pain Management approach. Instead of temporarily masking the symptoms or taking extreme measures, our protocol consists of a combination of safe and effective treatment solutions to address the root cause of the pain. This whole-person approach involves using the following methods to provide long-term pain relief:
Electroanalgesia
Electroanalgesia is a pain management technique that uses high-pulse electrical current to ease pain, boost blood circulation, improve mobility, and induce...
IV Therapy
IV nutritional therapy, or intravenous therapy, involves administering vital nutrients directly to the bloodstream through an IV. This type of treatment bypasses the digestive system, allowing for maximum absorption and utilization of nutrients by the...
Lifestyle Counseling
Lifestyle counseling is an approach to managing chronic pain that involves identifying, assessing, and modifying lifestyle factors contributing to an individual's pain. For example, lifestyle factors such as nutrition, physical activity, stress, sleep quality...
Start The Long-Term Pain Relief With Us
Osteoarthritis is a debilitating condition that can cause severe pain and discomfort. Unfortunately, surgery, medication, and chiropractic therapy often do not provide long-term pain relief and can be risky. We offer an interdisciplinary approach to treating this condition using a combination of non-surgical treatment options, such as electroanalgesia, specialized nutritional hydration, and lifestyle counseling. Our whole-person protocol is designed to address the root cause of the pain to provide long-term relief.
You don’t have to live in constant pain. Schedule a consultation and learn how we can help.